
Introduction
In recent years, the world of computing has witnessed a significant shift from traditional cloud computing to a paradigm known as “edge computing.” This transformation has been driven by the need for faster processing, real-time analysis, and decision-making capabilities in various industries. Edge computing is crucial for managing the data generated by connected devices and reducing strain on internet bandwidth and latency. Edge computing complements and enhances cloud capabilities by bringing computation and data storage closer to the source of data generation, resulting in reduced latency and improved response times. We will delve into the concept of edge computing, its importance, architecture, benefits, and real-world applications. We will also explore how the edge computing solutions developed by Acumera can empower businesses in this evolving landscape.
Understanding Edge Computing
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings data processing and computation closer to the data source, reducing the latency between data generation and analysis. Unlike traditional cloud computing, where data is processed in a central data center, edge computing leverages devices such as routers, gateways, and IoT devices to perform computations locally.
Complementing Cloud Capabilities
Edge computing complements cloud computing by extending its capabilities to the edge of the network. Edge-to-cloud computing enhances traditional centralized cloud computing by addressing challenges such as latency and bandwidth, processing data closer to its source. While cloud computing is ideal for processing and storing large volumes of data, edge computing is designed for real-time, low-latency processing. This synergy allows businesses to harness the benefits of both paradigms, enabling them to make faster decisions and improve overall efficiency. Additionally, evaluating strategies and technologies for edge deployments is crucial for ensuring performance, interoperability, and resilience.
Role of Edge Devices
Edge devices play a crucial role in edge computing by deploying computing and storage resources at the network edge, in close proximity to data sources. These devices, including routers, gateways, and IoT devices, collect and process data at the edge of the network. They act as intermediaries between the data source and the cloud, filtering and analyzing data before transmitting only relevant information to centralized data centers. Additionally, edge servers play a critical role in enhancing the performance of online and cloud utilization by minimizing lag and latency, significantly improving the overall customer experience.
Routers and gateways are both network devices, but they serve different purposes and have distinct functions within a network. Routers are primarily responsible for routing data packets between different networks based on IP addresses, while gateways serve as intermediaries between networks with differing protocols, translating data to ensure compatibility between the networks. The choice between using a router or a gateway depends on the specific networking requirements and the need for protocol translation within the network infrastructure. When combined with cloud computing, edge computing creates a powerful and flexible computing ecosystem that can address a wide range of application requirements in a connected world.
Why Edge Computing is Important
Edge computing holds immense significance in the modern technology landscape due to several compelling reasons:
Edge computing is important because it enables decentralized computing, which is critical for managing the vast amounts of data generated by modern applications. It facilitates faster, real-time data processing and mitigates network issues like bandwidth limitations and latency, making it essential for time-sensitive operations such as those in self-driving cars. Additionally, edge computing use cases demonstrate practical applications where data is collected and processed at or near the network edge, addressing challenges related to cost, technology limitations, and compliance issues.
Faster Processing and Real-time Analysis
One of the primary reasons for the rise of edge computing is its ability to enable faster processing and real-time analysis. By processing data locally at the edge, businesses can make instant decisions, leading to improved operational efficiency and enhanced user experiences.
One example of this is enhanced employee productivity, edge computing enables delivering the data employees need to do their jobs as efficiently as possible, and by keeping the equipment they use running smoothly without interruption.
Transformation Across Industries
Edge computing has the potential to transform businesses across every industry and function. Smart devices, along with edge computing, facilitate real-time monitoring, data processing, and automation to improve safety, productivity, and responsiveness. Whether it’s autonomous vehicles, hospitality, retail, healthcare, or industrial IoT, edge computing is driving innovation and revolutionizing how data is managed and utilized.
Imagine how collecting data from remote or inhospitable environments creates timely and actionable insights; whether it is data from underground fuel storage tanks that alert when the level is dropping unexpectedly, or a sensor on a freezer alerting a restaurateur that the temperature is rising.
Supporting Emerging Technologies
Edge computing is instrumental in supporting emerging technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT). AI algorithms can run locally on edge devices, providing real-time insights, while IoT devices can transmit data more efficiently, thanks to edge processing. In retail, AI is making great strides with edge computing in many areas. One common use case is providing store attendants the data they need to give instant recommendations based on a customer’s browsing and purchase history.
How Does Edge Computing Work?
Implementation Process
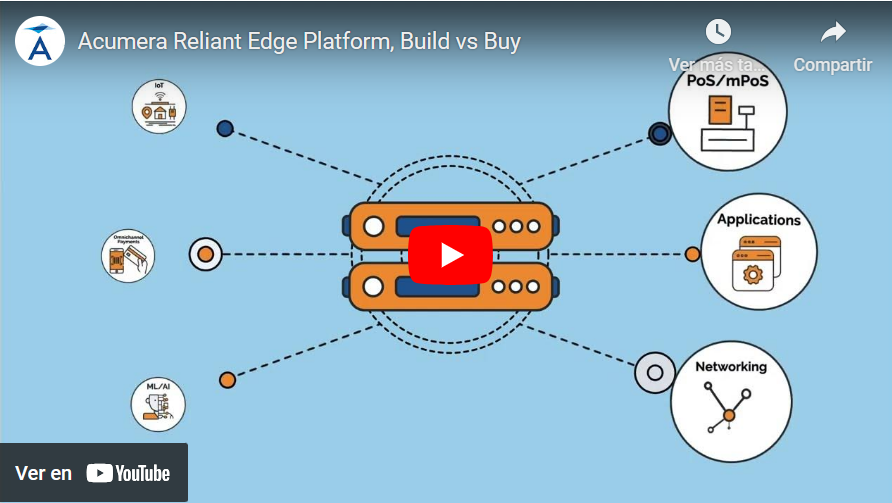
The implementation of edge computing involves deploying edge devices strategically within a network. These devices are equipped with the necessary processing power and storage capacity to handle data processing tasks locally. The Acumera Reliant Platform simplifies this process, offering ease of use and efficient management of edge computing resources, providing a turnkey approach to edge computing. Specifically, the Acumera Reliant Platform manages the following essential functions:
- Application Delivery – with a single intuitive user-interface, multiple diverse applications can be hosted and controlled simultaneously
- Configuration Management – by leveraging an open architecture that can interface with different API’s, configurations are easy to manage and enforce
- Orchestration – automates updates and configuration changes simplifying IT operations
- Monitoring – performance and availability alerts can be local or global
- Data Collection – data from every application, service, or device can be gathered for analysis, redirected, or forwarded
The Acumera Reliant Platform runs on standard, commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) hardware, allowing clients to select the optimal hardware for their needs. It is also cloud-agnostic, running on our secure cloud, the client’s private cloud or data center, or a third-party cloud provider of our client’s choosing.
Edge vs Cloud vs Fog Computing
Edge Computing
Edge computing focuses on processing data as close to the data source as possible. It offers low latency and real-time capabilities, making it suitable for applications that require quick decision-making.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing relies on centralized data centers for data processing and storage. It excels at handling large-scale data and batch processing but may introduce latency for time-sensitive applications.
Fog Computing
Fog computing is an intermediate approach that combines edge and cloud computing. It leverages edge devices to perform preliminary data processing, reducing the load on centralized data centers.
Edge Computing Benefits
Edge computing offers a range of benefits, including:
Reduced Latency and Improved Response Times
By processing data at the edge, edge computing significantly reduces latency, ensuring faster response times for critical applications.
Enhanced Security and Privacy
Local processing at the edge enhances security and privacy by minimizing the exposure of sensitive data to external networks.
Cost Savings
Edge computing reduces bandwidth requirements, resulting in cost savings for data transmission and storage. In addition, the Acumera Reliant Platform provides its customers significant improvements in the overall uptime of systems, reducing the number of trouble tickets, and providing faster recovery of service from hours and days to barely minutes. Recently, a customer with approximately 800-sites was able to reduce support incidents by over 40% since implementation.
Edge Computing Architecture
Hierarchical Architecture
Edge computing follows a hierarchical architecture that includes three primary layers:
- Edge Layer: This layer consists of edge devices such as sensors, gateways, and routers. It is the closest layer to the data source and performs initial data processing.
- Fog Layer: The fog layer acts as an intermediary between the edge and cloud layers. It performs more in-depth processing and aggregation of data before transmitting it to the cloud.
- Cloud Layer: The cloud layer represents centralized data centers where data can be further processed, stored, and analyzed at scale.
This architecture ensures efficient data flow and computation between these layers, optimizing the overall system’s performance.
Edge Computing Examples and Use Cases
Edge computing finds practical applications in various industries:
Retail
- Inventory Management: Edge devices or IoT sensors can continuously monitor product levels on store shelves. When items run low, the system can automatically generate restocking orders, ensuring that popular products are always available.
- Dynamic Pricing: Stores can use edge computing to adjust prices in real-time based on factors like demand, inventory levels, and competitor pricing. This dynamic pricing strategy can help maximize profits and minimize waste.
- Security and Surveillance: Edge AI cameras can be used for real-time surveillance, helping store owners detect theft, shoplifting, or suspicious behavior. Alerts can be sent immediately to store personnel or law enforcement when security breaches occur.
- Customer Analytics: Edge devices can capture and analyze customer data, such as foot traffic patterns, dwell times, and customer demographics. This information can help store owners optimize store layouts, product placement, and marketing strategies.
- Digital Signage and Advertising: Edge computing can power digital signage displays that dynamically change content based on real-time data. For example, advertising can be adjusted based on the time of day, weather conditions, or customer demographics.
- Customer Experience Enhancement: Edge devices can provide personalized experiences for customers by recognizing loyalty program members and offering tailored promotions or discounts in real-time.
Hospitality
- Point-of-Sale (POS) Systems: Edge computing at restaurant and bar POS systems ensures quick order processing and real-time updates for kitchen staff, improving customer service.
- Inventory Management: Edge devices track inventory levels in real time, helping restaurant staff restock ingredients and reduce waste by optimizing supply orders based on demand.
- Customer Feedback Analysis: Edge computing can analyze customer feedback and sentiment from online reviews and social media, providing insights that restaurants can use to improve their offerings promptly.
Industrial IoT (IIoT)
- Predictive Maintenance: In manufacturing, edge computing monitors equipment health by analyzing sensor data locally. It predicts maintenance needs, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Quality Control: Industrial cameras with edge processing can inspect product quality in real time, identifying defects and ensuring only high-quality products reach consumers.
Autonomous Vehicles
- Real-Time Navigation: Autonomous vehicles rely on edge computing to process sensor data, such as LiDAR and cameras, in real time to navigate and make instant decisions about steering, braking, and accelerating.
- Collision Avoidance: Edge computing helps detect potential obstacles and hazards on the road and enables the vehicle to react quickly to avoid collisions.
Smart Cities
- Traffic Management: In a smart city, edge devices at intersections can analyze traffic data locally to optimize traffic light timings and reduce congestion in real time.
- Public Safety: Smart surveillance cameras with edge computing can identify security threats, such as suspicious packages or unauthorized activities, and alert authorities immediately.
In all these scenarios, edge computing empowers real-time decision-making by processing data locally, reducing latency, and enabling immediate responses to critical situations and customer needs.
How Acumera’s Edge Computing Solutions Can Help Businesses
Edge computing is revolutionizing the way data is processed and delivered. By utilizing a distributed computing framework, it processes data closer to its source instead of relying solely on centralized servers or cloud locations. This approach enhances efficiency by situating computing resources, data storage, and applications nearer to the end-users who access the information.
The edge computing platforms created by Acumera are designed to simplify the workload and decision-making processes for organizations across industries. Here’s how we help businesses:
- Lower TCO:
- Reduced data transmission and bandwidth costs due to preprocessing and filtering data at the edge, and sending only relevant information to the cloud (1/100th to 1/1000th), resulting in significant cost savings related to bandwidth and cloud storage.
- Increasing IT productivity by automating repetitive tasks and streamlining back-office infrastructure, time to deploy new services is reduced (typically by more than 3x).
- Reduction in time needed to make configuration changes is typically reduced by more than 33%.
- Time needed to recover from failure is typically reduced by more than 24x.
- The Acumera Reliant Platform can be easily scaled to accommodate evolving business needs. Organizations can add more edge devices as required, without the complexity of overhauling their entire infrastructure.
- Reliability:
- Operations continue to operate if internet connectivity is lost, resulting in 2.7x fewer failures overall.
- Faster recovery from hardware, network, or software failures with fault-tolerant capability built in guaranteeing 100% uptime.
- Agility:
- Faster response times, which is crucial for applications requiring real-time decision-making
- The Acumera Reliant Platform makes it easy to deploy, manage and upgrade services. Users spend 75% less time managing and maintaining applications and report 46x more code deployments, which are direct measurements of an organization’s ability to respond in a fast-changing business environment.
- Enhanced Security and Compliance:
- The Acumera Reliant Platform improves security and data privacy by processing sensitive data at the edge. Data remains within the organization’s premises, reducing the risk of data breaches during transmission to the cloud. This is essential for businesses with strict compliance and data protection requirements.
- Support for Emerging Technologies:
- Our platforms seamlessly integrate with emerging technologies like AI and IoT and support businesses in harnessing the potential of these technologies.
The Acumera Reliant Platform empowers businesses by providing efficient edge computing resources, allowing them to harness the benefits of reduced latency, enhanced security, and cost savings.
In conclusion, edge computing is reshaping the way data is processed and analyzed, enabling faster decision-making, and driving innovation across various industries. As technology continues to advance, the role of edge computing in supporting emerging technologies like AI and IoT becomes increasingly critical. Learn more about how our edge computing platforms are poised to play a pivotal role in helping businesses leverage the advantages of this transformative paradigm.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Edge Computing:
What is edge computing in simple terms?
Edge computing refers to the practice of processing data closer to where it is generated, such as on local devices or nearby servers, rather than relying solely on a centralized data center. This reduces latency and allows for faster, more efficient data handling.
Who invented edge computing?
Edge computing evolved over time through contributions from various technology companies and researchers. There isn’t a single inventor, but it gained prominence as the need for real-time data processing in applications like IoT, autonomous vehicles, and industrial automation increased.
What problem does edge computing solve?
Edge computing addresses the challenge of latency and bandwidth limitations associated with cloud computing. By processing data closer to the source, it reduces the delay in data transmission, enhances real-time decision-making, and decreases the amount of data sent to centralized data centers.
What are the benefits of edge computing?
- Reduced Latency: Immediate data processing leads to quicker responses.
- Bandwidth Efficiency: Less data sent to the cloud reduces bandwidth usage.
- Enhanced Privacy: Sensitive data can be processed locally, improving security.
- Reliability: Local processing ensures that applications continue to function even with connectivity issues.
- Scalability: Efficiently manage large volumes of data generated by IoT devices.
Which situation would benefit the most by using edge computing?
Applications requiring real-time data processing and low latency benefit the most from edge computing. Examples include license plate identification in a QSR drive thru to offer loyalty rewards, or to enable car wash operations, kitchen display systems, or real time insights from cashier engagements with your customers, not just the more common examples of autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, smart cities, and healthcare monitoring systems.
What are some examples of edge computing?
- Personalized Marketing: By processing customer data locally, edge computing enables QSRs and retail stores to deliver personalized offers and promotions based on a customer’s purchase history and real-time behavior
- Digital Menu Boards: Edge computing can support the operation of dynamic digital menu boards that change based on factors like time of day, inventory levels, or customer preferences, all processed locally to reduce latency.
- Industrial IoT: Monitor and control machinery (like tank ATG’s or kitchen equipment) to optimize performance and predict maintenance needs., thus avoiding downtimeRetail: smart shelves equipped with sensors can monitor inventory levels in real-time and alert staff when restocking is needed. Edge computing processes this data on-site, ensuring faster responses and reducing out-of-stock situations.
- Real-Time Video/Voice Analytics: Edge computing enables real-time processing of surveillance video to detect suspicious activities, manage queues, and ensure safety compliance. This is crucial for both retail environments and QSRs, where immediate action can be required.
What is an example of an edge device?
An edge device can be any hardware that processes data locally. Examples include smart sensors like thermostats or door monitors), robots, gauges, cameras, autonomous vehicles, and network gateways.
Is edge computing safe?
Yes, edge computing can enhance security by processing sensitive data locally, reducing the risk of data breaches during transmission. With proper security measures such as encryption, authentication, and regular updates, edge computing can be a safe and reliable solution.




















4 thoughts on “What is Edge Computing: Transforming the Future of Data Processing”
Comments are closed.